Symptoms & Causes
Uterine Fibroids
Understanding the symptoms and causes of uterine fibroids can help determine which treatments to consider. Patients with fibroids may experience a range of symptoms or have no symptoms. Certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of developing fibroids. Some fibroids may be left untreated, but for those with troubling and painful symptoms of uterine fibroids, there are several treatment options available.
What are Uterine Fibroids?
What are Uterine Fibroids?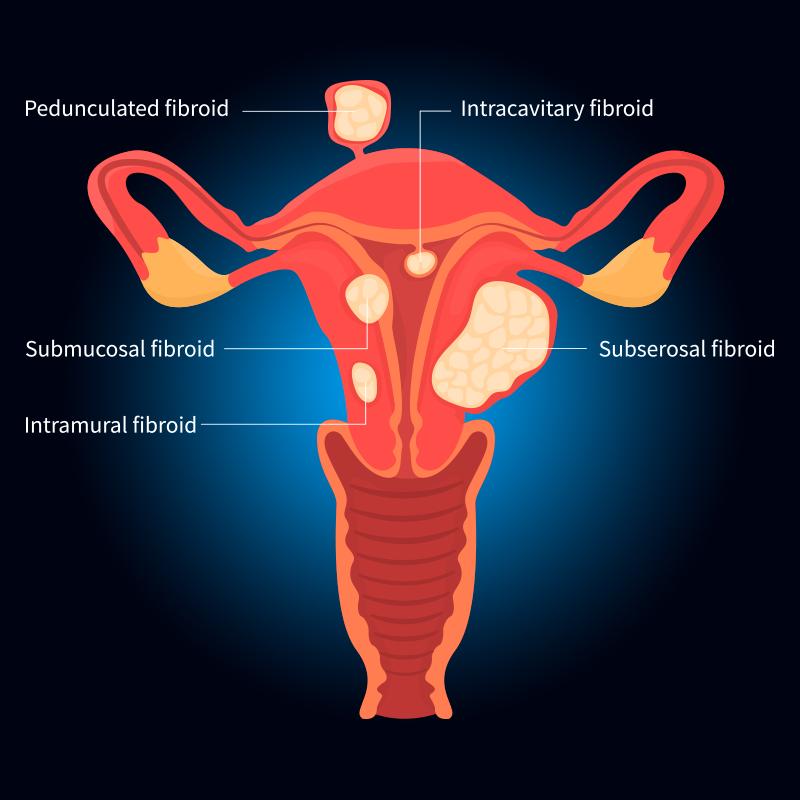
Uterine fibroids, also called uterine myomas or leiomyomas, are benign (noncancerous) tumors made up of muscle tissue and cells that develop in the uterus. The cause of uterine fibroids is not well understood, and a variety of factors have been examined, including ethnicity and age of the first period.
The sex hormones estrogen and progesterone also play an important role in the growth of fibroids. Early diagnosis and treatment by expert gynecologists can significantly help improve symptoms and reduce future health and fertility problems for all patients with fibroids.
Types of Fibroids
TypesYour doctor may detect several types of uterine fibroids during a physical examination or diagnostic procedure. These firm, compact connective tissue, and muscular cells are characterized by their location within the uterus.
The different types of fibroids include:
- Intramural fibroids which are located in the uterine wall
- Submucosal fibroids which are found in the uterine cavity
- Subserosal fibroids which are located on the uterine surface
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids
SymptomsUterine fibroids may be smaller than a pea and larger than a grapefruit. The size, amount, and location of fibroids can have different effects on a person’s symptoms. Common uterine fibroid symptoms include:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual periods
- Abnormal bleeding between menstrual periods
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Urinary frequency
- Abnormal bowel function
- Low back pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Abdominal bloating
- Anemia
- Reproductive problems
What Causes Uterine Fibroids?
CausesCauses of uterine fibroids, noncancerous growths, or tumors may vary. Experts believe that certain hormones, including estrogen and progesterone, may cause fibroids to grow at higher rates. In premenopausal people, there may be a greater risk of uterine fibroids due to increased estrogen levels in the body. Fibroids have been found to be more common in obese women and those of African American descent, but the reasons are unknown.
Risk Factors of Fibroids
Risk FactorsCertain factors can increase a person's chances of developing uterine fibroids. Early diagnosis and treatment for uterine fibroids can minimize symptoms. Seeing an expert gynecologist for routine examinations can help patients maintain their uterine health. Risk factors may include:
- Age (fibroids become more common during the 30s and 40s through menopause)
- Family history of fibroids
- Ethnicity (patients of African decent are more likely to develop fibroids)
- Obesity
- Diets high in red meat
Complications
ComplicationsIf left untreated, complications of uterine fibroids may include anemia and difficulty becoming pregnant, both due to heavy bleeding during menstrual periods. Uterine fibroids may affect fertility and childbirth and have been found to cause complications in conceiving, as well as miscarriage, labor complications, and premature labor. Pregnancy hormones may increase the rate of fibroid growth, and the location of fibroids may also play a role in these fibroid-related complications.
This content has been reviewed by the following medical editors.
Get Personalized Uterine Fibroid Care at NewYork-Presbyterian
At NewYork-Presbyterian, our team of board-certified gynecologists and gynecologic surgeons provide expert care for uterine fibroids. We offer a full range of comprehensive services to manage fibroids and your individual women's health needs. Contact us to make an appointment.



